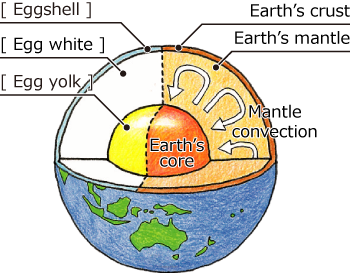
- The Earth’s Interior is Like a Boiled Egg
The Earth is divided into three layers—crust, mantle, and core—based on the differences in the materials that make up its interior. This structure can be compared to a boiled egg.
The mantle, which corresponds to the egg white, is solid but has fluid-like properties, moving slowly due to thermal convection caused by temperature differences. The crust and the uppermost part of the mantle, which correspond to the egg’s shell, form a rigid outer layer called the lithosphere, or “plate.” The Earth’s surface is made up of over a dozen moving plates.
- Plate Movements, Volcanoes, and Earthquakes
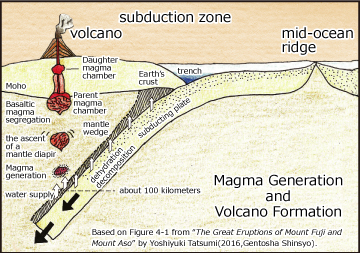
The area around the Japanese archipelago is unique in that four tectonic plates collide and interact, a rarity on Earth. Among these, the Pacific Plate, the largest plate on Earth, is dragged by mantle convection and subducts at the Japan Trench. This subduction causes friction with other plates, leading to the formation of volcanoes and the occurrence of earthquakes.
Magma, the source of volcanic activity, forms when water carried into the Earth’s interior by the subduction of the Pacific Plate lowers the melting point of rocks deep beneath the Japanese archipelago. The magma rises due to buoyancy, and when it reaches the surface, volcanic activity occurs.
- The Location Where Bandai Volcano Was Born
Since magma forms only after the subducting plate reaches a certain depth, volcanoes are distributed in a line at a fixed distance from the trench. In the Tohoku region, this horizontal distance is about 300 km to the west of the trench. This volcanic line is called the “volcanic front,” and the volcanoes of the Ou Mountain Range belong to it. Mt. Bandai is one of the volcanoes located on this volcanic front.

